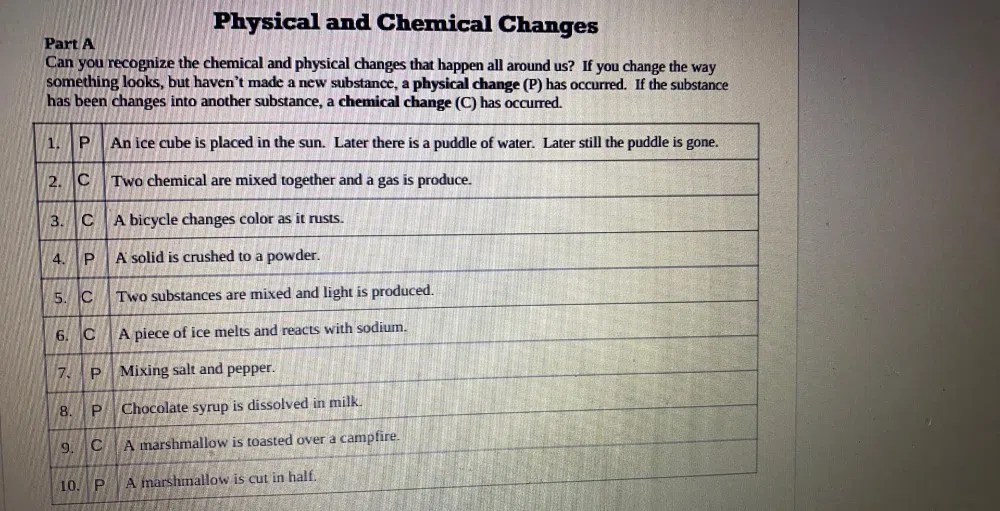
A bicycle changes color as it rusts. – As a bicycle changes color as it rusts, it embarks on a captivating journey of transformation, inviting us to unravel the intricate interplay between chemistry and aesthetics. This discourse delves into the scientific underpinnings of rust’s chromatic dance, exploring its impact on bicycle components and its artistic allure.
The oxidation process that gives rise to rust triggers a kaleidoscope of color changes, from the vibrant hues of orange to the deep, earthy tones of brown. Understanding the factors that govern these color shifts empowers us to appreciate the unique patina that time and the elements bestow upon our beloved bicycles.
Color Changes in Rusting Bicycles
The rusting of a bicycle is a common sight, especially in areas with high humidity or exposure to moisture. Rust is a reddish-brown coating that forms on iron and steel when exposed to oxygen and water. The color changes associated with rusting are due to the formation of different iron oxides, which have varying colors.
Initially, the surface of the bicycle will develop a thin layer of rust, which appears as a light brown or orange color. As the rusting process progresses, the layer of rust thickens and darkens, turning into a deep reddish-brown color.
In some cases, the rust may also develop a greenish tint due to the formation of iron hydroxides.
Factors Influencing Color Change
The rate and extent of color change in rusting bicycles are influenced by several factors, including:
- Exposure to moisture:Rusting occurs in the presence of moisture, so bicycles exposed to high humidity or frequent rainfall will rust more quickly.
- Temperature:Rusting is accelerated at higher temperatures, so bicycles exposed to warm or hot climates will rust more rapidly.
- Presence of salt:Salt can accelerate the rusting process, so bicycles exposed to saltwater or deicing agents will rust more quickly.
- Type of metal:Different types of metal rust at different rates. For example, steel rusts more quickly than stainless steel.
Impact of Rust on Bicycle Components: A Bicycle Changes Color As It Rusts.
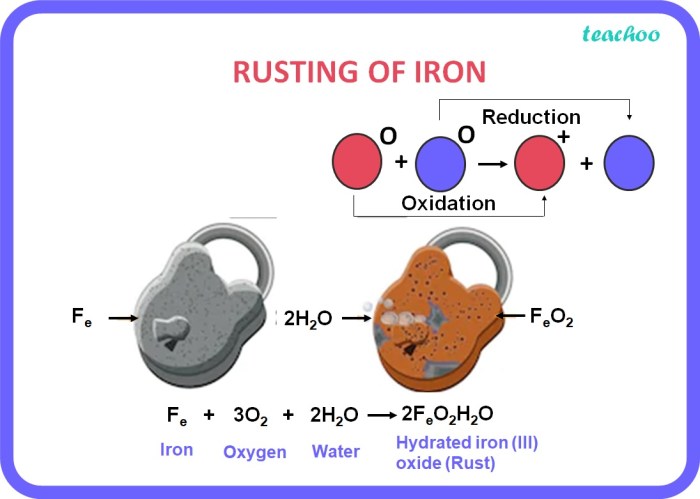
Rust, the result of iron oxidation, poses significant threats to bicycle components, affecting their integrity and functionality. This section delves into the specific effects of rust on various bicycle components and provides insights into its detrimental consequences.
Frame
The bicycle frame, typically made of steel or aluminum, is highly susceptible to rust. Rust can cause the frame to weaken, compromising its structural integrity. In severe cases, it can lead to frame failure, posing safety risks to the rider.
Moreover, rust can spread rapidly, affecting other components connected to the frame.
Handlebars
Handlebars, often made of steel or aluminum, are another common target of rust. Rust can weaken the handlebars, making them more prone to bending or breaking during use. This can result in loss of control and potential accidents.
Wheels
Bicycle wheels, including rims, spokes, and hubs, can also be affected by rust. Rust on rims can weaken them, increasing the risk of punctures or blowouts. Rusted spokes can compromise wheel stability, leading to wobbling and potential accidents. Similarly, rust on hubs can affect bearing performance, resulting in increased friction and premature wear.
Prevention and Mitigation, A bicycle changes color as it rusts.
To prevent or minimize rust on bicycles, several measures can be taken:
- Regular cleaning and drying of the bicycle to remove dirt and moisture
- Application of rust-resistant coatings or lubricants
- Regular inspections for signs of rust and prompt treatment
li>Storing the bicycle in a dry and well-ventilated area
Artistic Implications of Rusting Bicycles
Rusting bicycles possess a unique aesthetic appeal that has captured the attention of artists and designers. The patina of rust creates a distinctive visual texture and color, adding character and depth to the bicycle’s form.
The symbolism associated with rusted bicycles is equally compelling. Rust represents the passage of time and the transformative power of nature. It evokes a sense of nostalgia and decay, yet also suggests resilience and adaptability.
In Art and Design
Rusted bicycles have been incorporated into a variety of artistic creations. Sculptures, paintings, and installations often feature bicycles as a central motif, exploring themes of time, decay, and the human condition.
Examples
- The American artist Tom Sachs has created a series of sculptures using rusted bicycles, commenting on consumerism and the disposability of modern objects.
- The British artist Damien Hirst has used rusted bicycles in his installations, exploring themes of mortality and the fragility of life.
Rust Prevention and Removal Techniques
Rust prevention and removal are crucial aspects of bicycle maintenance to ensure longevity and optimal performance. By implementing appropriate techniques, cyclists can effectively safeguard their bicycles from corrosion and restore them to pristine condition when rust occurs.
Rust Prevention Methods
Preventing rust on bicycles involves proactive measures to minimize exposure to moisture and corrosive elements. Some effective methods include:
- Protective Coatings:Applying rust-resistant coatings, such as paint, lacquer, or wax, creates a protective barrier against moisture and oxygen.
- Galvanization:Coating steel components with zinc protects them from rust by forming a sacrificial layer that corrodes instead of the steel.
- Storing in Dry Environments:Keeping bicycles in dry, well-ventilated areas minimizes exposure to moisture that promotes rust.
Rust Removal Techniques
Removing rust from bicycles requires careful consideration of the affected components and the severity of corrosion. Several techniques are commonly employed:
- Chemical Treatments:Applying rust-removing chemicals, such as vinegar or commercial rust removers, dissolves the oxide layer and facilitates its removal.
- Mechanical Methods:Using abrasive materials like sandpaper, wire brushes, or steel wool physically removes rust by scraping or grinding it away.
- Electrolysis:Submerging rusted components in a solution of water and baking soda and passing an electric current through it converts rust into a more easily removable form.
It is important to note that rust removal techniques should be applied with caution to avoid damaging the underlying metal. Proper cleaning and protection after rust removal are also essential to prevent recurrence.
Essential Questionnaire
Why does a bicycle change color as it rusts?
Rusting is an electrochemical process that occurs when iron is exposed to oxygen and moisture. As the iron oxidizes, it forms iron oxide, which is the reddish-brown substance we know as rust. The color of rust can vary depending on the type of iron oxide that forms.
Can I prevent my bicycle from rusting?
Yes, there are several things you can do to prevent your bicycle from rusting. These include:
- Keeping your bicycle clean and dry
- Applying a protective coating to the metal parts of your bicycle
- Storing your bicycle in a dry place
How can I remove rust from my bicycle?
There are several ways to remove rust from your bicycle. These include:
- Using a commercial rust remover
- Applying a vinegar solution to the rusty area
- Using a wire brush to scrub away the rust