Diffusion and osmosis crossword answer key – Welcome to the fascinating world of diffusion and osmosis, where we delve into the intricate processes that govern the movement of molecules across cellular membranes. Embark on an engaging journey as we explore the concepts, factors, and relationship between these fundamental biological phenomena.
Our ultimate destination: the diffusion and osmosis crossword answer key, where knowledge solidifies and understanding blooms.
Diffusion, the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, plays a vital role in countless biological processes. From the exchange of gases in the lungs to the absorption of nutrients in the digestive system, diffusion ensures the constant replenishment of essential substances.
Osmosis, a specialized form of diffusion involving water molecules, governs the movement of water across semipermeable membranes. It maintains cellular hydration, regulates blood pressure, and facilitates nutrient transport in plants.
Diffusion and Osmosis: Diffusion And Osmosis Crossword Answer Key
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental processes that play crucial roles in various biological and physical systems. Understanding these processes is essential for comprehending the functioning of cells, tissues, and organs.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules or particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process occurs until equilibrium is reached, where the concentration becomes uniform throughout the system.
Examples of diffusion in everyday life include the spreading of perfume in a room, the movement of gases in the atmosphere, and the absorption of nutrients by plant roots.
Factors that affect the rate of diffusion include:
- Concentration gradient: The greater the concentration difference, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to a faster rate of diffusion.
- Surface area: A larger surface area increases the contact between substances, facilitating faster diffusion.
- Diffusion distance: The longer the distance over which diffusion must occur, the slower the rate of diffusion.
Osmosis
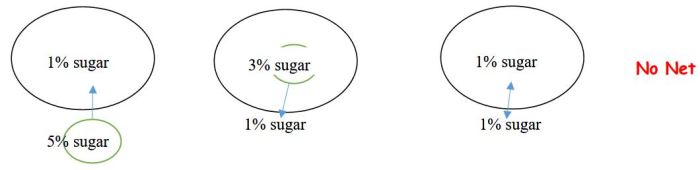
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through but restricts the passage of other molecules or particles.
The process of osmosis can be explained using the following steps:
- A semipermeable membrane separates two solutions of different concentrations.
- Water molecules move from the solution with lower solute concentration (higher water concentration) to the solution with higher solute concentration (lower water concentration).
- This movement continues until the water concentration is equal on both sides of the membrane, resulting in osmotic equilibrium.
Factors that affect the rate of osmosis include:
- Concentration gradient: The greater the concentration difference between the two solutions, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of water molecules, leading to a faster rate of osmosis.
- Surface area of the membrane: A larger surface area increases the contact between the solutions, facilitating faster osmosis.
- Thickness of the membrane: A thinner membrane reduces resistance to water flow, leading to a faster rate of osmosis.
Relationship between Diffusion and Osmosis, Diffusion and osmosis crossword answer key
Diffusion and osmosis are closely related processes. Diffusion is the general movement of molecules or particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion and osmosis work together in many biological systems. For example, the diffusion of oxygen into the blood from the lungs occurs through the process of osmosis. Similarly, the diffusion of nutrients into cells from the bloodstream also involves osmosis.
Questions Often Asked
What is the primary driving force behind diffusion?
Diffusion occurs due to the concentration gradient, the difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas.
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
Osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane, while diffusion encompasses the movement of any molecules across a concentration gradient.
What factors influence the rate of osmosis?
The rate of osmosis is affected by factors such as the concentration gradient of water, the permeability of the membrane, and temperature.