Hardware lab simulation 1-3 using motherboard connectors – Embark on a comprehensive journey through Hardware Lab Simulations 1-3, where the intricacies of motherboard connectors unravel. From understanding their purpose and exploring their diverse types to witnessing their practical applications, this exploration delves into the foundational elements that orchestrate seamless computer system functionality.
As we delve into the intricacies of CPU installation, thermal paste application, and the vast array of CPU coolers, we unravel the secrets behind a computer’s computational prowess. Memory installation, encompassing various types and compatibility considerations, unveils the significance of choosing the right components for optimal performance.
Hardware Lab Simulation 1: Motherboard Connectors

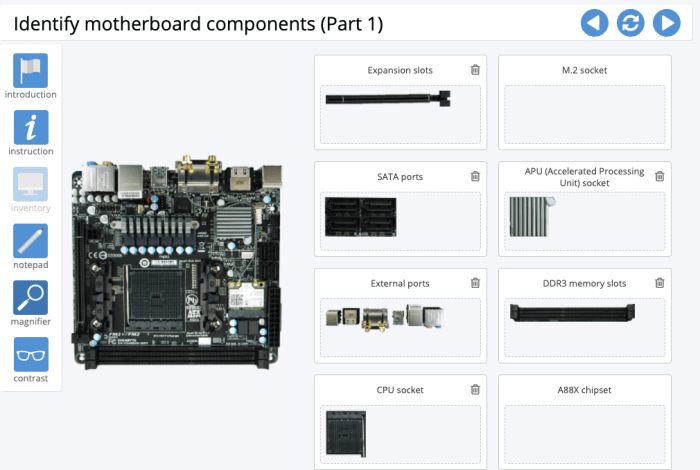
Motherboard connectors are essential components of a computer system, providing the physical interface between the motherboard and other components. They enable data and power transfer between the motherboard and devices such as processors, memory, storage drives, and expansion cards.
Types of Motherboard Connectors
There are various types of motherboard connectors, each designed for a specific purpose:
- CPU Socket: Connects the processor to the motherboard.
- Memory Slots: Accommodate memory modules (RAM).
- PCIe Slots: Allow the installation of expansion cards, such as graphics cards and sound cards.
- SATA Ports: Connect storage devices, such as hard disk drives and solid-state drives.
- Power Connectors: Supply power to the motherboard and other components.
Examples of Motherboard Connector Usage
Motherboard connectors play a crucial role in connecting various components within a computer system:
- The CPU socket establishes a connection between the processor and the motherboard, allowing data and instructions to be processed.
- Memory slots enable the installation of memory modules, which store data and instructions temporarily during processing.
- PCIe slots allow the expansion of the computer system’s capabilities by accommodating additional hardware, such as graphics cards for enhanced visual performance.
- SATA ports connect storage devices to the motherboard, enabling data storage and retrieval.
- Power connectors provide electrical power to the motherboard and other components, ensuring their proper functioning.
Hardware Lab Simulation 2: Installing a CPU

Installing a CPU is a critical step in building a computer system. It requires careful handling and attention to detail to ensure proper functionality.
Steps Involved in Installing a CPU, Hardware lab simulation 1-3 using motherboard connectors
The process of installing a CPU involves the following steps:
- Open the CPU socket leveron the motherboard.
- Align the CPUwith the socket, ensuring the arrow indicator on the CPU matches the corresponding mark on the socket.
- Carefully lower the CPUinto the socket and close the lever to secure it.
- Apply thermal pasteto the top of the CPU to improve heat transfer.
- Install the CPU coolerto dissipate heat generated by the CPU during operation.
Importance of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste plays a crucial role in CPU installation by enhancing heat transfer between the CPU and the CPU cooler. It fills in microscopic gaps between the two surfaces, reducing thermal resistance and ensuring efficient cooling.
Types of CPU Coolers
There are two main types of CPU coolers:
- Air Coolers: Use fans to dissipate heat from the CPU.
- Liquid Coolers: Circulate a liquid coolant through a radiator to dissipate heat more effectively.
Hardware Lab Simulation 3: Installing Memory
Installing memory is essential for providing the computer system with sufficient storage capacity for data and instructions.
Steps Involved in Installing Memory
Installing memory involves the following steps:
- Open the memory slot leverson the motherboard.
- Align the memory modulewith the slot, ensuring the notch on the module matches the corresponding ridge in the slot.
- Push down on both endsof the memory module until it clicks into place.
- Close the memory slot leversto secure the module.
Types of Memory
There are various types of memory used in computer systems:
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory): The most common type of memory, used for temporary storage of data and instructions.
- SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): Faster than DRAM but more expensive, used in cache memory.
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): Non-volatile memory that stores permanent data, such as the BIOS.
Importance of Using the Correct Memory Type
Using the correct type of memory for your motherboard is crucial for ensuring compatibility and proper system functioning. Motherboards support specific memory types, such as DDR4 or DDR5, with different speeds and capacities. Using incompatible memory can result in system instability or failure.
Key Questions Answered: Hardware Lab Simulation 1-3 Using Motherboard Connectors
What is the purpose of motherboard connectors?
Motherboard connectors serve as communication channels between the motherboard and various components, enabling data transfer, power supply, and device functionality.
What are the different types of motherboard connectors?
Motherboard connectors encompass a wide range, including CPU sockets, memory slots, expansion slots, and peripheral connectors, each designed for specific component interfacing.
How do I troubleshoot hardware issues related to motherboard connectors?
Troubleshooting motherboard connector issues involves inspecting connections, ensuring proper component seating, and checking for any physical damage or debris that may hinder functionality.