Give the percent yield when 28.16 g of co2 – In chemistry, understanding the concept of percent yield is crucial. This article delves into the significance of percent yield calculations, providing a comprehensive guide to determine the efficiency of chemical reactions. Beginning with a practical example of calculating percent yield using 28.16 g of CO2, we will explore the essential steps, considerations, and applications of percent yield in various fields.
Percent yield serves as a valuable tool for chemists, chemical engineers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers, enabling them to optimize industrial processes and ensure the efficient production of desired products. By understanding the factors that influence percent yield, researchers can minimize errors and maximize the yield of their reactions, leading to advancements in various scientific and industrial domains.
Percent Yield: Give The Percent Yield When 28.16 G Of Co2

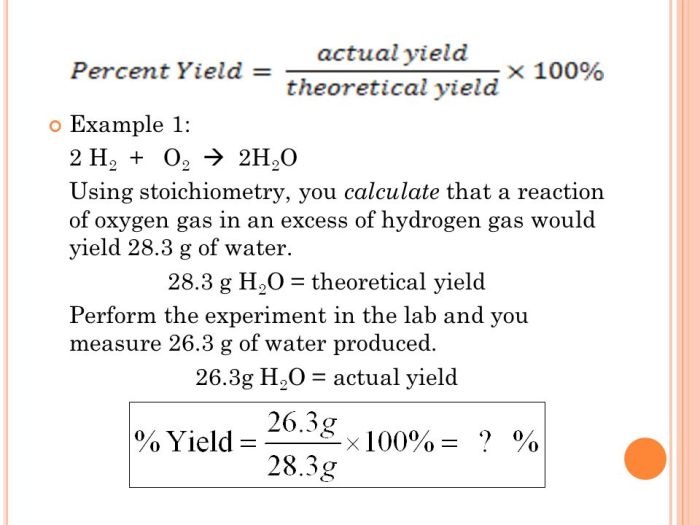
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction. It is calculated by dividing the actual yield of a reaction by the theoretical yield and multiplying the result by 100. The theoretical yield is the amount of product that would be produced if the reaction went to completion, while the actual yield is the amount of product that is actually obtained.
Percent yield is an important concept in chemistry because it allows chemists to assess the efficiency of their reactions. A high percent yield indicates that the reaction is efficient and that the desired product is being produced in a high yield.
A low percent yield indicates that the reaction is inefficient and that the desired product is not being produced in a high yield.
Reaction Stoichiometry, Give the percent yield when 28.16 g of co2
The stoichiometry of a reaction is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. The balanced chemical equation shows the mole ratio between the reactants and products of the reaction. The mole ratio can be used to calculate the theoretical yield of the reaction.
Calculations
The theoretical yield of a reaction is calculated by multiplying the moles of the limiting reactant by the mole ratio between the limiting reactant and the desired product. The actual yield of a reaction is determined by measuring the amount of product that is actually obtained.
The percent yield of a reaction is calculated using the following formula:
“`Percent yield = (Actual yield / Theoretical yield) x 100“`
Experimental Considerations
There are a number of factors that can affect the percent yield of a reaction. These factors include the temperature of the reaction, the concentration of the reactants, and the presence of catalysts. It is important to control these factors in order to obtain a high percent yield.
Applications
Percent yield is used in a variety of fields, including chemical engineering and pharmaceutical manufacturing. In chemical engineering, percent yield is used to optimize the efficiency of chemical reactions. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, percent yield is used to ensure that the desired drug is being produced in a high yield.
Example Problem
A student reacts 28.16 g of CO2 with excess carbon to produce CO. The student obtains 15.00 g of CO. What is the percent yield of the reaction?
| Substance | Moles |
|---|---|
| CO2 | 0.640 mol |
| CO | 0.375 mol |
The theoretical yield of CO is 0.640 mol – (1 mol CO / 1 mol CO2) = 0.640 mol CO.
The percent yield of the reaction is (0.375 mol / 0.640 mol) x 100 = 58.6%.
Helpful Answers
What is the formula for calculating percent yield?
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100%
What factors can affect percent yield?
Purity of reactants, reaction conditions, side reactions, and experimental errors
How is percent yield used in industrial processes?
To optimize production efficiency, minimize waste, and ensure product quality